Does Ammonia Kill Mold? Ammonia as a Mold Killer: Does it Work?

Does Ammonia Kill Mold? This is a question that many homeowners face when dealing with mold problems in their living spaces. Mold development can be commonplace, especially in areas of excessive humidity or damage by water. Mold does not just look ugly but also poses health hazards to those living in the affected areas. Ammonia is a widely used household cleaner and is often cited as a way to eliminate mold. But is it effective?
In the following article, we’ll examine the efficacy of ammonia’s ability to kill mold, and then discuss its possible advantages and disadvantages. We will explore the scientific basis behind ammonia’s anti-mold properties and discuss the best ways to use it. We will also provide useful suggestions for preventing the growth of mold and provide other solutions for removing mold. No matter if you’re faced with a minor mold issue or an extensive problem, knowing the importance of ammonia in removing mold is essential to ensure the health of your family and living space.
Read More: Is Drywall Flammable?
What is Mold? Does ammonia kill black mold?
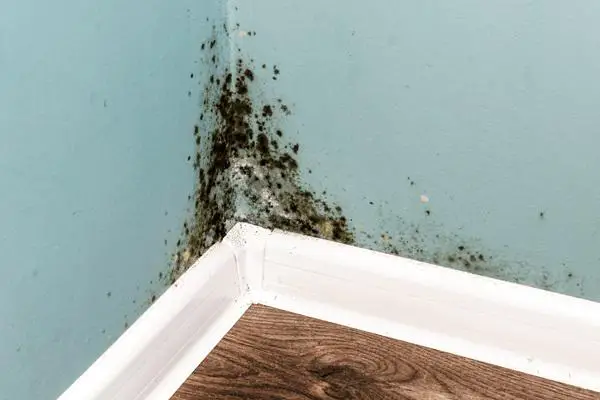

Mold is a frequent problem that a lot of us have had to deal with at one point or another. It’s the unsightly fuzzy growth that you see on damp surfaces like walls, ceilings, or even food. But what exactly is it and why does it appear to appear from the blue? Here, we’ll look into the nature of mold and its various kinds, and how it impacts our lives. So, let’s begin!
Understanding Mold
Mold is a kind of fungus that thrives best in moist conditions. It reproduces by the release of tiny spores into the air that can be deposited and grow on a variety of surfaces. They are everywhere, both outdoors and indoors, and are able to find them in our homes through the windows or doors, as well as on our clothes.
Different Types of Mold

Mold is found in a variety of types that each have their particular characteristics and health dangers. Let’s look at the most common kinds of mold:
1. Alternaria

The Alternaria is a common mold located in damp areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, or basements. Its appearance is dark black or brownish-black spots and is a smooth texture. Inhalation of Alternaria may cause allergic reactions and worsen asthma symptoms in those who are sensitive.
2. Mucor
Mucor is a rapidly growing mold that flourishes in humid environments that contain organic materials such as food that is decaying or insulation that is wet. It is a greyish or white appearance, as well as a cotton-like feel. Although it’s generally non-toxic people with weak immune systems can be afflicted with respiratory issues after exposure to Mucor.
3. Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a typical indoor mold that can appear in many colors, such as green brown, yellow, or black. It is often found on ceilings, walls, or other household items, particularly in humid environments. Although most varieties of Aspergillus are non-toxic, however, some of them produce mycotoxins that could cause respiratory problems and allergic reactions.
4. Penicillium
The Penicillium is a blue-green mold that is often found on fabrics like wallpaper, carpets, and other textiles. It is quickly spread and creates an unpleasant odor. Certain species of Penicillium release mycotoxins that could cause respiratory issues and allergic reactions.
5. Trichoderma

The Trichoderma is a mold that has a greenish color and thrives in environments that are humid and contain cellulose substances, such as paper or wood. It is a cause of respiratory problems and allergic reactions in people who are at risk. Trichoderma is also noted for its capacity to fight off and limit the growth of other molds.
6. Stachybotrys

The Stachybotrys often called black mold is a dark blackish-green species of mold found in places that are prone to prolonged humidity, like water-damaged structures or after flooding. The mold produces mycotoxins and the exposure to these toxins could cause respiratory issues as well as other health problems.
7. Acremonium
The Acremonium is a type of mold that usually appears as powdery substances that range in hues from orange to pink. It is often found in drain pans, humidifiers, or window sealants. Acremonium is a source of mycotoxins that can trigger a range of health issues, such as respiratory problems and skin infections.
The Impact of Mold on Health
Exposure to mold may have negative effects on our well-being, particularly for those with asthma, allergies, or weakened immune systems. The most common signs of exposure to mold can include sneezing, coughing, eye irritation, wheezing as well as skin irritation. Excessive exposure to specific kinds of mold and their mycotoxins could cause more severe respiratory conditions and allergic reactions or even infections.
Preventing and Managing Mold Growth

Prevention is crucial in the fight against mold. Here are some guidelines to help you stop and manage the growth of mold within your home:
– Make sure your living areas are well-ventilated to decrease the humidity levels.
Fix any water leaks immediately.
– Make use of dehumidifiers in areas that are prone to water.
Clean regularly and dry areas susceptible to dampness, for example, kitchens and bathrooms.
Avoid carpeting in damp areas, like basements.
– Ensure adequate ventilation in the kitchen and bathroom when you are doing actions that produce humidity, like showering or cooking.
How to deal with Mold

If you find mold within your home, you must take action quickly and efficiently. Here are some guidelines to take:
- Determine the type of form of the mold: Determine the kind of mold that you’re working with, either through an inspection of the visual or consulting a certified mold expert.
- Protect the affected area: Reduce the spreading of spores from mold isolating the affected region. Close windows and doors and cover vents using plastic sheets.
- Be safe: Use protective equipment including goggles, gloves, and a respirator mask to protect yourself from direct exposure to mold and its spores.
- Eliminate the mold: Based on the severity of the mold infestation, you can remove tiny areas of mold using a mixture of detergent and water or a mold remover that is specialized. For more extensive problems, it’s recommended to seek out a mold remediation expert.
- Repair the root of the issue: Find the cause of the moisture that created mold. Repair any leaks, increase ventilation, or take any other measures to prevent the occurrence of mold issues.
If you’re not sure about how to deal with mold growth, or if the region affected is huge it is always recommended to consult a professional to ensure the correct remediation.
Why Does Mold Grow?
Mold is a result of being in the vicinity of water in the right temperature range and organic matter to consume. Moisture is the main factor that triggers the growth of mold. It can be caused by a variety of sources like leaks, extreme humidity levels, condensing, and water damage. When materials or surfaces remain wet for a long time, it creates the perfect environment for mold spores to expand and settle. In addition, it thrives in temperatures that range from 68degF-86degF (20degC between 30 and 40degC). This temperature range is typically seen in many indoor environments. In addition, mold requires organic matter such as wood or drywall to provide food to support its expansion. When all the conditions are aligned the mold spores begin to germinate and then begin to grow in the area, which leads to the visible growth of mold.
Does Ammonia Kill Mold and How to Use It?
When confronted by a mold issue homeowners often wonder whether ammonia is an effective remedy. Ammonia is a mold-killer however it’s crucial to be aware of its efficacy and limitations as well as the best way to utilize it. Let’s look into this topic more thoroughly.
The Effectiveness of Ammonia in Killing Mold

Ammonia is a powerful cleaning agent that kills mold on surfaces that are not porous. It does this by altering pH levels, which makes the surroundings unsuitable for the growth of mold. The alkaline nature of ammonia creates a favorable environment in which molds struggle to survive. It’s crucial to remember that ammonia works the most effectively at battling surfaces and does not be able to penetrate deep into the porous material in which mold may grow.
Proper Usage of Ammonia to Kill Mold

For ammonia to be effective in mold removal, use these steps:
1. Safety Precautions:
Before beginning cleansing, make sure you are taking the proper precautions to protect yourself. Wear protective gloves, goggles, and a mask to shield yourself from harmful fumes as well as the possibility of coming into contact with mold and spores.
2. Dilution:
Ammonia should be always diluted prior to use. Mix one-third ammonia with one-third water to make an effective and safe cleaning solution.
3. Ventilation:
Make sure that there is adequate ventilation in the area in which you’ll work. Make sure you open the windows and use fans to circulate fresh air since ammonia fumes are extremely irritating and bothersome.
4. Surface Preparation:
Take away any visible or loose growing mold from the affected area prior to the application of the ammonia solutions. Make use of a scrubber or a clean cloth to take away the mold debris.
5. Application:
Use a sponge or cloth to dip into the ammonia solution that has been diluted and then apply it to the affected area. Clean the area thoroughly making sure you cover all affected mold areas.
6. Dwell Time:
Let the ammonia solution remain at the top of your surface for a couple of minutes. This will ensure greater absorption and efficiency against mold.
7. Rinse and Dry:
After the time has passed then wash the surface using clear water to get rid of the ammonia solution along with any remaining mold spores. Dry the surface completely with the aid of a fan or opening windows to stop any further accumulation of moisture.
8. Dispose of Materials:
Clean up any cleaning supplies, like cloths or sponges employed during your cleaning procedure. Put the bag with plastic, then dispose of them in a proper manner to stop contamination.
Limitations and Considerations of Ammonia to Kill Mold
Although ammonia is effective in eliminating mold on non-porous surfaces it is not suitable or appropriate for every mold situation. Here are some guidelines and issues to bear in your mind:
Penetration Limits: Ammonia may not penetrate far into porous materials like carpeting or drywall in which mold may develop below the surface. In these cases, professional mold remediation might be required.
Toxicity: Ammonia releases strong fumes which can cause irritation to the eyes or nose as well as throat. Make sure you have adequate ventilation throughout the cleaning process and do not mix ammonia, bleach, or any other cleaning chemicals since it may release toxic gasses.
Safety Precautions: Use appropriate precautions to avoid exposure to ammonia, such as wearing protective equipment and avoiding direct contact with eyes or skin.
Alternative Solutions: There are other products for killing mold that could be more appropriate for certain conditions or even materials. It is always beneficial to study and evaluate alternatives before you decide to use ammonia as your main solution.
Some Precautions to Take While Using Ammonia to Kill Mold
Ammonia can be an effective instrument to tackle mold problems However, it’s essential to use it with care. There are a few precautions to take into consideration when using ammonia for killing mold. If you follow these tips you can guarantee your safety as well as maximize the efficiency of your cleaning process.
Pros of Using Ammonia to Kill Mold

Before we get into the safety precautions we’ll first discuss some advantages of Using Ammonia to Kill Mold
1. Effectiveness in battling Surface Mold:
Ammonia is a well-known chemical for its capability to destroy the growth of mold that is found on surfaces with no pores. It alters the pH making a place where mold is unable to thrive.
2. Cost-effective Solution:
Ammonia is a widely available and inexpensive cleaning agent, making it a great option for the removal of mold.
3. Easy to Use:
Utilizing ammonia to remove mold is an easy procedure. Mix it up then apply it to the area affected and scrub, rinse, and dry.
Cons of Using Ammonia to Kill Mold
Although ammonia is a great product it’s important to take into consideration the following drawbacks and limitations. disadvantages:
1. Limited Penetration:
Ammonia can not penetrate completely into porous materials like carpeting or drywall in which mold may develop below the surface. This could result in the incomplete elimination of mold and the possibility of growth.
2. Toxic Fumes:
Ammonia releases powerful fumes that can cause irritation to the nose, eyes, and throat. It’s essential to provide adequate ventilation throughout the cleaning process. Use fans, open windows, and think about wearing a mask to shield yourself from dust.
3. Chemical Interaction:
Avoid mixing ammonia and bleach with other cleaning chemicals. Combining them can result in dangerous gases, such as chlorine gas or chloramine, that can be very harmful to your health.
4. Skin and Eye Irritation:
Ammonia can cause eye and skin irritation after contact. It is essential to wear gloves that are protected and safety glasses when handling ammonia in order to avoid direct exposure.
5. Environmental Impact:
Ammonia is a powerful chemical, and its incorrect disposal could cause negative impacts on the natural environment. Be sure to dispose of it properly by following the local guidelines and regulations.
Precautions to Take While Using Ammonia to kill mold

To protect yourself and maximize the efficacy of ammonia to remove mold There are some safety tips to remember:
1. Read and Follow Instructions:
Be sure to read the instructions on the ammonia label prior to use. Be sure to follow the recommended dilution ratios and guidelines for use provided by the manufacturer.
2. Ventilate the Area:
A proper ventilation system is vital when working with ammonia. It is important to open the windows and doors for fresh air to circulate. You may want to consider using fans to enhance the flow of air.
3. Use Protective Gear:
Wear safety gloves, goggles, and a mask to protect your face from direct contact with ammonia and its vapors. This will prevent eye and skin irritation and reduce the inhalation of fumes.
4. Test a Small Area First:
Before applying ammonia over a larger area, test it in an inconspicuous, small area to ensure that it doesn’t cause damage or discoloration to the surface. This will allow you to determine if it is compatible with the surface you’re working on.
5. Dilute Ammonia Properly:
Always dilute ammonia using water in accordance with recommendations for ratios. If Ammonia in pure form can be too harsh and can harm surfaces or cause further problems.
6. Beware of mixing Ammonia with other chemicals:
Don’t mix ammonia with bleach or cleaners. The combination could result in toxic gasses that pose major health hazards.
7. Follow Cleaning Procedures:
Clean the affected area thoroughly with the ammonia solution dilute. The surface should be scrub gently but firm enough to get rid of the mold spores. Allow the solution to stand for a couple of minutes to improve its effectiveness prior to rinsing.
8. Proper Disposal:
Get rid of all cleaned-up materials like sponges or cloths, by sealing them in a plastic bag. Make sure you follow the local rules for the correct disposal procedures for ammonia as well as its products.
Final Words
Ammonia is an effective strategy to fight the growth of surface mold. But, it is essential to take the necessary steps to ensure your safety and get the most effective outcomes. Make sure you air-condition the area, wear safety gear, and do not mix ammonia and other chemicals. Be aware of the limitations, particularly when dealing with porous substances or large infestations of mold. If you’re unsure or struggling with a difficult mold problem is advisable to seek help from a professional. If you approach ammonia use in a responsible manner it is possible to successfully fight mold and provide a healthier living space.



